1.800.858.7378npic@oregonstate.edu
Call, email, or chat Mon-Fri
A to Z

Why does NPIC write fact sheets?
NPIC's mission is to provide objective, science-based information about pesticides and pesticide-related topics. We create fact sheets to help people get the information they need to make informed decisions about pesticides and their use.
The goal of NPIC fact sheets is to provide objective information on pesticides. We base them on the best scientific sources that are available at the time we write them. We follow set standards to identify reliable sources of information. The fact sheets are reviewed carefully to make sure that information is understood and cited correctly. Fact sheets are not intended to be a complete literature review of a subject. They are also not intended to cover all related laws and regulations.
How does NPIC find scientific studies?
Fact sheets are meant to represent broad scientific agreement at the time we write them. We use a variety of sources to find the information we include in a fact sheet (Table 1). We first look for overviews such as handbooks and reviews. These reviews represent agreement among the people who know the most about the subject. NPIC is not able to review all of the science to write a review ourselves. NPIC only uses or cites work that has been written by independent science organizations and that has been peer reviewed. NPIC also uses data from government risk assessments. These assessments are available to the public. Studies used in risk assessments must follow strict standards called Good Laboratory Practices (GLPs).
If we can't find any overviews or government documents, we look at peer-reviewed scientific literature for trends. We judge research papers on their methods and whether their results support the conclusions. To find information, NPIC staff use databases such as PubMed of the National Library of Medicine, TOXLINE, Web of Science, Academic Search Premier, and others available through Oregon State University’s library services.
How do I find when fact sheets were written?
Each NPIC fact sheet has a date that indicates when it was completed. NPIC does not have the capacity to maintain all of its fact sheets entirely up-to-date. However, nearly all of the information remains current except possibly for potential health effects.
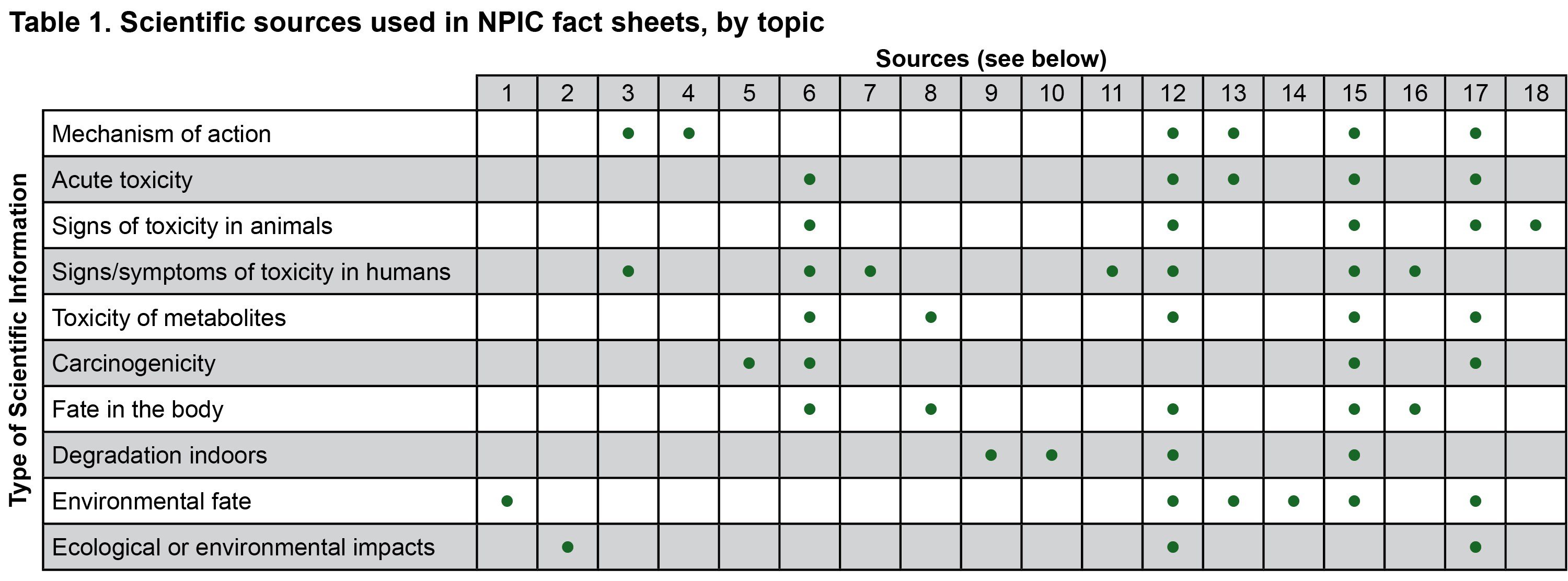
Sources (see table above):
- CDPR Environmental Fate Reviews
- EPA's ECOTOX
- Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology, Academic Press (various editions)
- Herbicide Handbook, Weed Science Society of America (various editions)
- IARC Monographs, World Health Organization (WHO)
- JMPR Reports and Evaluations, World Health Organization (WHO)/Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
- Medical case studies
- Metabolic Pathways of Agrochemicals, Royal Society of Chemistry (various editions)
- EPA's Center for Public Health and Environmental Assessment studies
- EPA's Office of Research and Development online studies
- Occupational Studies, PubChem Hazardous Substances Databank (HSDB)
- Open literature
- The Pesticide/Biopesticide Manual, British Crop Protection Council (various editions)
- Pesticide Properties Database
- Publicly available EPA documents
- Recognition and Management of Pesticide Poisonings
- Toxicology texts
- Veterinary texts
These sources may be used when available:
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR, part of CDC)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- National Academy of Sciences (NAS)
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, part of CDC)
- National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS, part of NIH)
- National Toxicology Program
- WHO International Programme on Chemical Safety (IPCS)
Where can I get more information?
For more detailed information about NPIC fact sheets call the National Pesticide Information Center, Monday - Friday, at 800-858-7378, or visit us on the web at npic.orst.edu. NPIC provides objective, science-based answers to questions about pesticides.
Gervais, J.; Cross, A., Buhl, K.; Jenkins, J. 2020. Writing NPIC Fact Sheets; National Pesticide Information Center, Oregon State University Extension Services. http://npic.orst.edu/factsheets/review.html

NPIC fact sheets are designed to answer questions that are commonly asked by the general public about pesticides that are regulated by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA). This document is intended to be educational in nature and helpful to consumers for making decisions about pesticide use.
